Level services,problems and protocols
Network Layer
- The Network Layer is the third layer of the OSI model.
- It handles the service requests from the transport layer and further forwards the service request to the data link layer.
- The network layer translates the logical addresses into physical addresses
- It determines the route from the source to the destination and also manages the traffic problems such as switching, routing and controls the congestion of data packets.
- The main role of the network layer is to move the packets from sending host to the receiving host.
Services Provided by the Network Layer
- Guaranteed delivery: This layer provides the service which guarantees that the packet will arrive at its destination.
- Guaranteed delivery with bounded delay: This service guarantees that the packet will be delivered within a specified host-to-host delay bound.
- In-Order packets: This service ensures that the packet arrives at the destination in the order in which they are sent.
- Guaranteed max jitter: This service ensures that the amount of time taken between two successive transmissions at the sender is equal to the time between their receipt at the destination.
- Security services: The network layer provides security by using a session key between the source and destination host. The network layer in the source host encrypts the payloads of datagrams being sent to the destination host. The network layer in the destination host would then decrypt the payload. In such a way, the network layer maintains the data integrity and source authentication services.
Network Layer Protocols
ARP
- ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol.
- It is used to associate an IP address with the MAC address.
- Each device on the network is recognized by the MAC address imprinted on the NIC. Therefore, we can say that devices need the MAC address for communication on a local area network. MAC address can be changed easily. For example, if the NIC on a particular machine fails, the MAC address changes but IP address does not change. ARP is used to find the MAC address of the node when an internet address is known.
How ARP works?
If the host wants to know the physical address of another host on its network, then it sends an ARP query packet that includes the IP address and broadcast it over the network. Every host on the network receives and processes the ARP packet, but only the intended recipient recognizes the IP address and sends back the physical address. The host holding the datagram adds the physical address to the cache memory and to the datagram header, then sends back to the sender.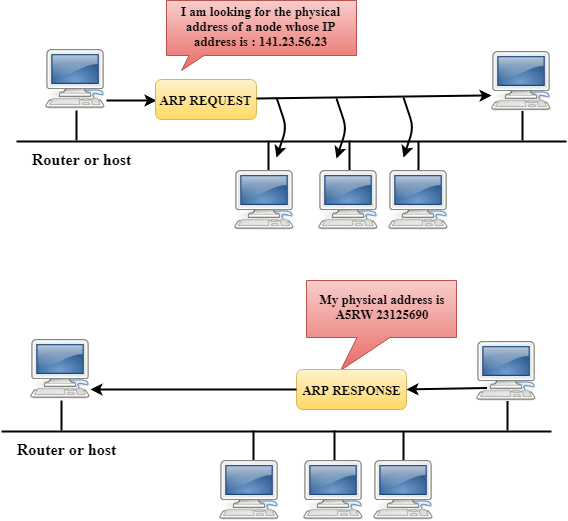
Steps taken by ARP protocol
If a device wants to communicate with another device, the following steps are taken by the device:- The device will first look at its internet list, called the ARP cache to check whether an IP address contains a matching MAC address or not. It will check the ARP cache in command prompt by using a command arp-a
- If ARP cache is empty, then device broadcast the message to the entire network asking each device for a matching MAC address.
- The device that has the matching IP address will then respond back to the sender with its MAC address
- Once the MAC address is received by the device, then the communication can take place between two devices.
- If the device receives the MAC address, then the MAC address gets stored in the ARP cache. We can check the ARP cache in command prompt by using a command arp -a.
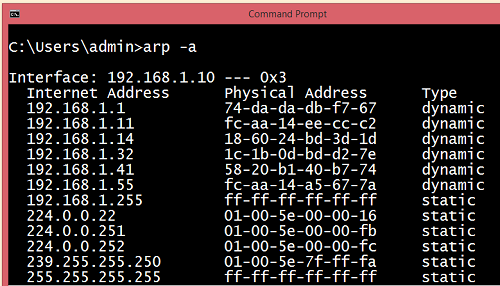
There are two types of ARP entries:
- Dynamic entry: It is an entry which is created automatically when the sender broadcast its message to the entire network. Dynamic entries are not permanent, and they are removed periodically.
- Static entry: It is an entry where someone manually enters the IP to MAC address association by using the ARP command utility.
RARP
- RARP stands for Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
- If the host wants to know its IP address, then it broadcast the RARP query packet that contains its physical address to the entire network. A RARP server on the network recognizes the RARP packet and responds back with the host IP address.
- The protocol which is used to obtain the IP address from a server is known as Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
- The message format of the RARP protocol is similar to the ARP protocol.
- Like ARP frame, RARP frame is sent from one machine to another encapsulated in the data portion of a frame.

ICMP
- ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol.
- The ICMP is a network layer protocol used by hosts and routers to send the notifications of IP datagram problems back to the sender.
- ICMP uses echo test/reply to check whether the destination is reachable and responding.
- ICMP handles both control and error messages, but its main function is to report the error but not to correct them.
- An IP datagram contains the addresses of both source and destination, but it does not know the address of the previous router through which it has been passed. Due to this reason, ICMP can only send the messages to the source, but not to the immediate routers.
- ICMP protocol communicates the error messages to the sender. ICMP messages cause the errors to be returned back to the user processes.
- ICMP messages are transmitted within IP datagram.
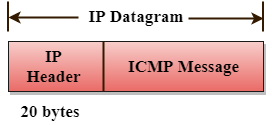
The Format of an ICMP message

- The first field specifies the type of the message.
- The second field specifies the reason for a particular message type.
- The checksum field covers the entire ICMP message.
Error Reporting
ICMP protocol reports the error messages to the sender. Five types of errors are handled by the ICMP protocol: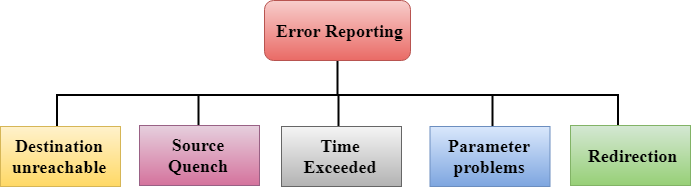
- Destination unreachable: The message of "Destination Unreachable" is sent from receiver to the sender when destination cannot be reached, or packet is discarded when the destination is not reachable.
- Source Quench: The purpose of the source quench message is congestion control. The message sent from the congested router to the source host to reduce the transmission rate. ICMP will take the IP of the discarded packet and then add the source quench message to the IP datagram to inform the source host to reduce its transmission rate. The source host will reduce the transmission rate so that the router will be free from congestion.
- Time Exceeded: Time Exceeded is also known as "Time-To-Live". It is a parameter that defines how long a packet should live before it would be discarded.
- Parameter problems: When a router or host discovers any missing value in the IP datagram, the router discards the datagram, and the "parameter problem" message is sent back to the source host.
- Redirection: Redirection message is generated when host consists of a small routing table. When the host consists of a limited number of entries due to which it sends the datagram to a wrong router. The router that receives a datagram will forward a datagram to a correct router and also sends the "Redirection message" to the host to update its routing table.
IGMP
- IGMP stands for Internet Group Message Protocol
- The IP protocol supports two types of communication:
- Unicasting: It is a communication between one sender and one receiver. Therefore, we can say that it is one-to-one communication.
- Multicasting: Sometimes the sender wants to send the same message to a large number of receivers simultaneously. This process is known as multicasting which has one-to-many communication.
- The IGMP protocol is used by the hosts and router to support multicasting.
- The IGMP protocol is used by the hosts and router to identify the hosts in a LAN that are the members of a group.
- IGMP is a part of the IP layer, and IGMP has a fixed-size message.
- The IGMP message is encapsulated within an IP datagram.
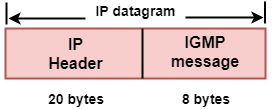
The Format of IGMP message
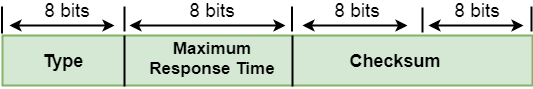
Where
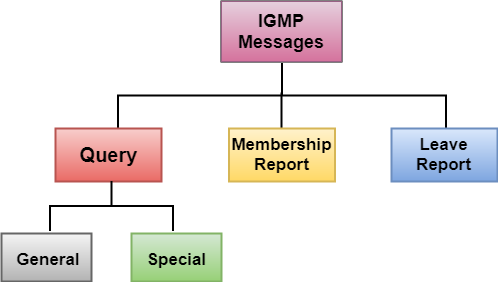
Type: It determines the type of IGMP message. There are three types of IGMP message: Membership Query, Membership Report and Leave Report.
Maximum Response Time: This field is used only by the Membership Query message. It determines the maximum time the host can send the Membership Report message in response to the Membership Query message.
Checksum: It determines the entire payload of the IP datagram in which IGMP message is encapsulated.
Group Address: The behavior of this field depends on the type of the message sent.
- For Membership Query, the group address is set to zero for General Query and set to multicast group address for a specific query.
- For Membership Report, the group address is set to the multicast group address.
- For Leave Group, it is set to the multicast group address.